HiddenLayer’s Model Scanner integrates with Databricks Unity Catalog to automatically scan ML models for vulnerabilities.
HiddenLayer integrates with Unity Catalog to automatically scan ML models for vulnerabilities, using the HiddenLayer Model Scanner. Getting started is simple, just run the command-line installer (CLI) on either Windows or macOS to install the HiddenLayer integration (read the rest of this guide for details).
Models registered with the Unity Catalog Model Registry can be scanned. The Unity Catalog organizes models in catalogs, and within each catalog there are schemas. During the CLI installation, you will choose a schema. New model versions in that schema will be scanned automatically. Scan results are recorded as tags in the model registry.
Once you input the necessary parameters, the job will be set up and ready to run. However, if you wish to customize the job further, it will require some familiarity with Databricks and its configurations.
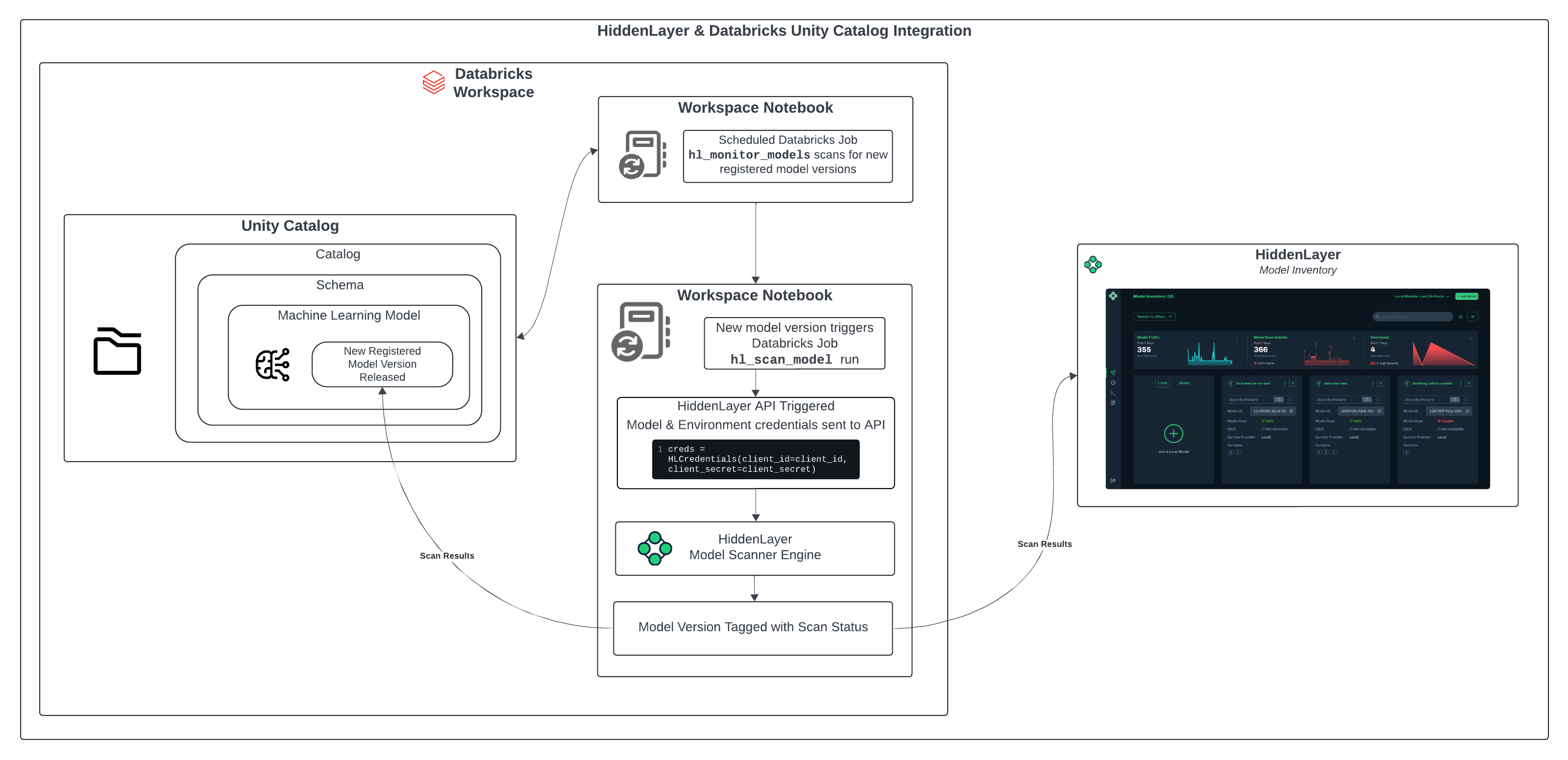
The CLI installer sets up two Python notebooks in a HiddenLayer folder in your Databricks workspace. The hl_monitor_models notebook runs periodically as a scheduled job, looking for new model versions in the specified Unity Catalog schema. When it finds a new model version, it runs the hl_scan_model notebook, which sends models to the HiddenLayer scanner and records the results.
Example of a workspace folder:
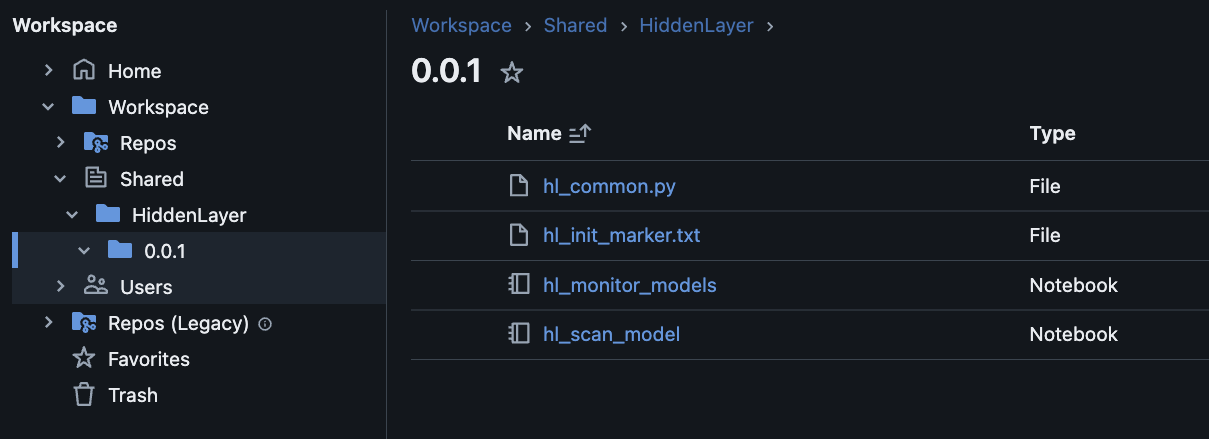
Inside the HiddenLayer folder is a folder named according to the software version. The folder contains the two notebooks (hl_monitor_models and hl_scan_model), and two additional files.
hl_common_pyis code shared by the notebookshl_init_marker.txtis used to track that one-time initialization has happened
This job continuously monitors the selected catalog and schema for new model versions. When new versions are detected, it triggers a new job that scans the models in parallel using the HiddenLayer model scanner. The results will be shown on the model version tag, and a model card will be created in your HiddenLayer console. By default, the job scans for new model versions every 12 hours.
The HiddenLayer Databricks integration works with AWS, Azure, and GCP cloud providers.
The following are required to integrate the HiddenLayer Model Scanner with Databricks Unity Catalog.
Unity Catalog: Choose the catalog/schema holding models to be scanned.
Databricks cluster: Choose or create a compute cluster to run the HiddenLayer integration.
Databricks authentication: Ensure that you have your Databricks workspace URL and either a personal access token available or the path to the token cache file.
HiddenLayer authentication: Choose or create an API key for your account and have available the client ID, and client secret.
- Note: Your HiddenLayer API client ID and client secret have an expiry. When these expire, scan jobs will start failing with authentication errors. To resolve this, generate a new HiddenLayer API client ID and client secret, then update the Databricks secret store. Do not change the secret name because this is part of the Databricks job configuration.
- When creating your API key, you will be able to set specific permissions for the key (according to the principle of least privilege). For the Databricks integration, the following permission sets are needed: Model Inventory read/write, Model Scanner write.
Have the following information ready before starting the installation: Databricks, Databricks Compute, and Permissions.
URL: The workspace URL for your Databricks instance.
Databricks Authorization Credentials, which could be either:
- OAuth with Databricks CLI - Authenticate with
databricks auth login --host <databricks_host>you must provide a full path to the token cache file generated by databricks, for example/Users/<username>/.databricks/token-cache.json - Personal Access Token (PAT): Used to authenticate access to Databricks resources. Link to the Databricks PAT documentation.
- OAuth with Databricks CLI - Authenticate with
Catalog: The name of the Unity Catalog to scan.
Schema: The schema the models are registered in.
Compute: The ID for the cluster running the jobs; must have UC access.
Client ID: HiddenLayer API Client ID. Link to console: HiddenLayer API US or HiddenLayer API EU.
- Note: if using a self-hosted instance of Model Scanner, you will have to generate this via API.
Client Secret: HiddenLayer API Client Secret.
- Note: if using a self-hosted instance of Model Scanner, you will have to generate this via API.
If using a HiddenLayer instance other than the default US SaaS console:
- Your HL region, OR
- the endpoint for your self-hosted deployment of Model Scanner
HiddenLayer scans are executed in the cloud, whether using the SaaS or on-prem deployment. The Databricks cluster does not perform the actual scan or analysis.
Instead, the cluster is responsible for:
- Downloading the model from MLflow
- Temporarily storing the model artifacts
- Uploading the files to HiddenLayer via API
- Tagging the model version in the MLflow Model Registry
Below are recommended compute specifications. These may need to be adjusted depending on the number of workers and the number or size of models in your Unity Catalog schema.
- Cluster Policy: Can be Personal or Shared, but whichever is selected, the notebook job must have permission to run the cluster.
- Databricks Runtime Version: 16.1 (Scala 2.12, Spark 3.5.2)
- Node Type: Standard_DS4_v2 (28 GB memory, 8 cores)
- Auto-Termination: Set to terminate after 120 minutes of inactivity, as the job will start and stop the compute as needed.
Note: These specs are intentionally conservative. In many cases, this configuration may be overprovisioned. If you observe that the job runs quickly and without memory or network bottlenecks, you can safely size down the cluster to reduce cost.
Integrating the HiddenLayer Model Scanner with Databricks Unity Catalog requires appropriate access and configurations in both platforms. Databricks users must ensure permissions to manage clusters, secret scopes, and catalog/schema access. HiddenLayer users must maintain valid API credentials for model scanning.
To integrate HiddenLayer Model Scanner with Databricks Unity Catalog, the following permissions are required:
Tagging Permissions:
- Grant
APPLY TAGpermissions on the object that needs to be tagged. - Grant
USE SCHEMApermissions on the object’s parent schema. - Grant
USE CATALOGpermissions on the object’s parent catalog.
- Grant
Databricks Cluster Permissions
- Cluster Management: Grant
Can Managepermissions for the compute cluster used in the integration.
- Cluster Management: Grant
Databricks Secrets Management
- Secrets Access: Ensure
Can ReadandCan Managepermissions on the secret scope storing the HiddenLayer API credentials (client ID and client secret).
- Secrets Access: Ensure
Authentication
- Workspace Authentication: Access to the Databricks workspace with a valid personal access token.
To configure and use the HiddenLayer Model Scanner, the following permissions are required:
API Key Management
- Ensure access to create and manage API keys within the HiddenLayer account.
Installation options:
- SaaS Model Scanner
- Self-hosted (on-prem) Model Scanner
Credentials are stored in the Databricks secret store for secure use by the integration.
Download the HiddenLayer Installer for your specific operating system. Unzip the contents and choose the specific script for your machine.
- For example, choose hiddenlayer-databricks-model-scanner_Darwin_arm64 for running on a Apple Silicon Machine.
Using a terminal, navigate to the appropriate directory and run the installation command in the folder of the downloaded installer.
./hldbx autoscanNote: Depending on your network and system settings, you may need admin permissions to allow the script to run.
When prompted, enter your Databricks host URL. For example:
https://adb-1234567890123456.7.azuredatabricks.net.You will be prompted to enter the path to the token cache file.
You can either enter the pathway to the file, OR
Enter your Databricks personal access token. The token is hidden for security purposes.
- A “successfully authenticated to Databricks” message should display.
Enter the ID for the Databricks compute cluster that will run the integration.
To find your compute cluster ID, click into your compute cluster, select the three dots in the top right hand corner, click “View JSON”, then copy the compute ID in the top line of the JSON file.
- A confirmation message about finding the Databricks cluster should display.
Optionally, you can provide the Service Principal ID to run the job under.
- Note that the Compute Run As and Job Run As must be the same person or service principal. Set the Service Principal ID here to match the one used for the compute instance.
At this point, you are given the option to set the number of concurrent scans (default: 10). Hit Enter to accept the default (can be changed later in the UI), or enter your desired number of concurrent scans.
You’ll then be prompted to set the default scanning interval (default: 12 hrs). Hit Enter to accept the default (can be changed later in the UI), or enter a quartz cron expression to change to your desired interval.
Enter the Unity Catalog name to scan.
Enter the catalog schema.
- A confirmation message for the selected schema and catalog should display.
Repeat the selection process for additional catalogs and schemas, or hit Enter to continue.
- If you add additional catalogs here, they will be added to the same job, i.e. one job will be created in Databricks to scan multiple locations.
Select your HiddenLayer API location:
For tenants in the US:
USFor tenants in the EU:
EUFor self-hosted instances:
CUSTOM- For
CUSTOMyou will then be prompted to provide the appropriate URL.
- For
Enter your HiddenLayer API Client ID.
Enter your HiddenLayer API Client Secret. The client secret is hidden for security purposes.
Enter a name for the Databricks Secret that will be used to store HiddenLayer API key. Example: my_api_key.
- A "Successfully authenticated to HiddenLayer" message should be displayed. Return to your Databricks Console to confirm that the job has been set up correctly.
Monitoring for new model versions starts after the integration is installed. Any model files existing in the schema prior to the integration are tagged as unscanned. This is to prevent potentially scanning a large number of existing files. You can delete this tag and the monitoring job will see the model as new and scan it.
To see the scan results, view the tags.
To see scan results, navigate to the model version in the Databricks Catalog Explorer.
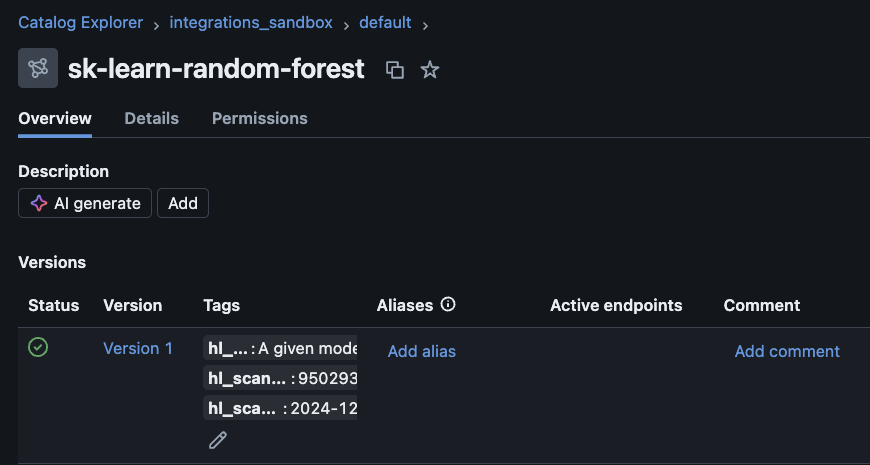
Move the mouse over the Tags area, then click the Edit button (pencil icon). The tags display. See the table below for information about these tags.
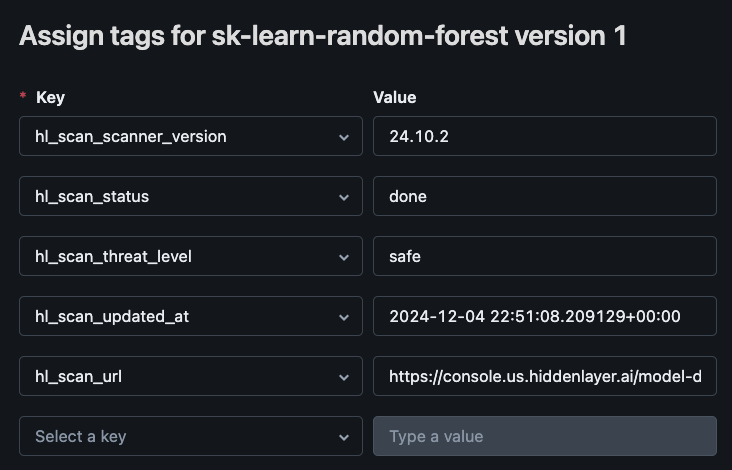
You can also view the scan results in the HiddenLayer AISec Platform Console: HiddenLayer Console US or HiddenLayer Console EU.
- In the Console, the file names are modified to improve viewing them on the Model Inventory page.
- In the Unity Catalog, the full name is
<catalog>.<schema>.<model>. - In the Console, the name is
<model>.<schema>.<catalog>. - This is done so the model name appears first on the Model Inventory page.
| Key | Values | Description |
|---|---|---|
| hl_scan_status | pending, done, failed, or unscannned |
|
| hl_scan_scanner_version | <version> | The version of the HiddenLayer Model Scanner. |
| hl_scan_threat_level | safe, low, medium, high, critical, or unknown | The scan threat level for the model. |
| hl_scan_updated_at | <timestamp> | The date and time the scan finished. |
| hl_scan_url | <console_url> | The URL to the HiddenLayer Console where you can see full details about the scan. |
To manually trigger the hl_find_new_model_versions job in Databricks, follow the steps below to initiate the process and monitor its execution.
Navigate to Job Runs:
- Log in to your Databricks workspace.
- On the left-hand side of the screen, click on the Jobs icon to open the job management section.
Click on the Jobs Tab:
- Once you're in the Jobs section, ensure you are in the Jobs tab to view the list of available jobs.
Locate the Job:
- Scroll through the list of jobs or use the search functionality to find the job named
hl_find_new_model_versions.
- Scroll through the list of jobs or use the search functionality to find the job named
Run the Job:
- Next to the job name
hl_find_new_model_versions, click on the play button (▶️) under the Run Now column to manually start the job.
- Next to the job name
Wait for Execution:
- After clicking Run Now, the job will begin executing. You can monitor the progress under the Job Runs tab.

These instructions guide you through modifying job parameters in Databricks, including the API key, catalogs and schemas, schedules, triggers, and compute instance, all within the right-hand panel of the job details page.
Navigate to Job Runs:
- Log in to your Databricks workspace.
- On the left-hand side of the screen, click on the Jobs icon to open the job management section.
Go to the Jobs Tab:
- Ensure you are in the Jobs tab where all available jobs are listed.
Select the Job:
- Find the job you want to modify and click on the hl_find_new_model_versions to open its details.
Access the Right-Hand Panel:
Once you’ve opened the job details, navigate to the right-hand side panel. Here, you will find several configurable parameters, including:
- HiddenLayer API Key: The key used to access the HiddenLayer API.
- Catalogs and Schemas: The data catalogs and schemas that the job monitors.
- Schedules and Triggers: The scheduling and trigger settings for job execution.
- Compute Instance: The compute instance the job will use for execution.
Modify Parameters:
- You can configure or adjust any of these parameters directly in the right-hand panel. Make sure to save your changes after making adjustments.
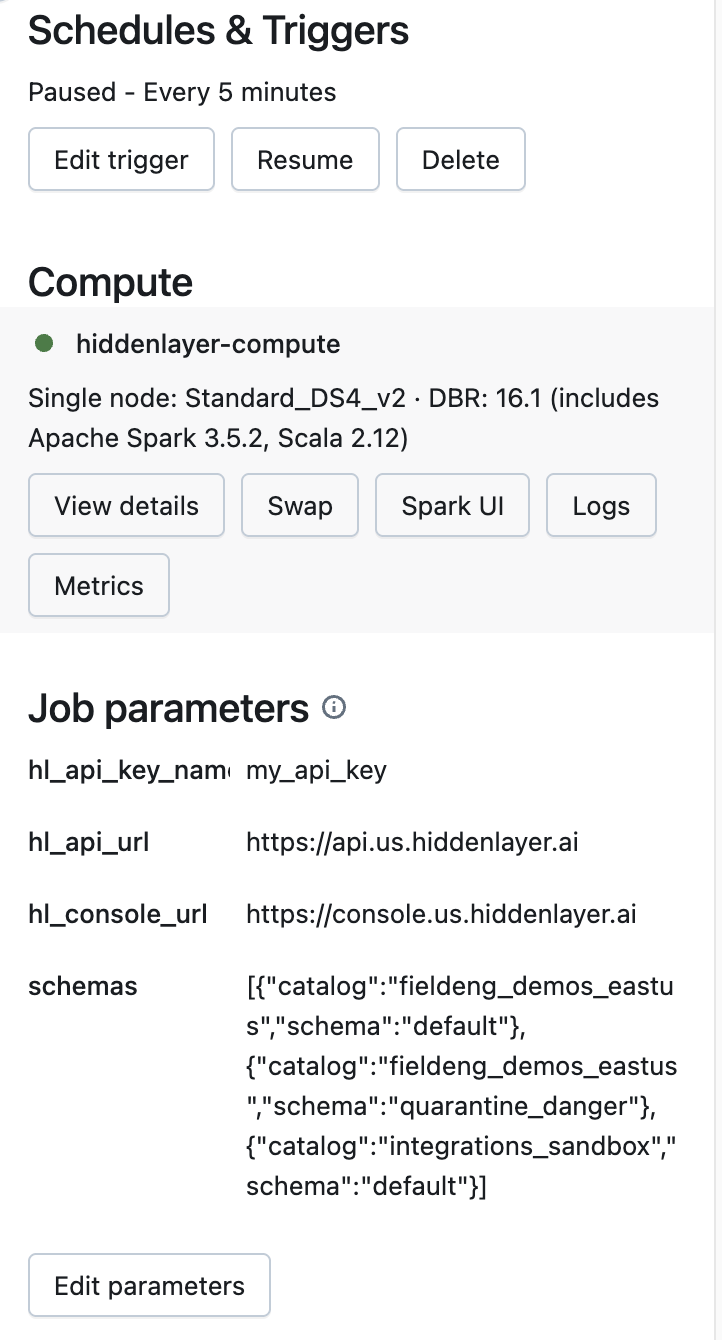
Update the scan interval based on what you need.
From the job overview, go to the "Job Details” panel on the left and look for “Schedules and Triggers”. Click Edit trigger.
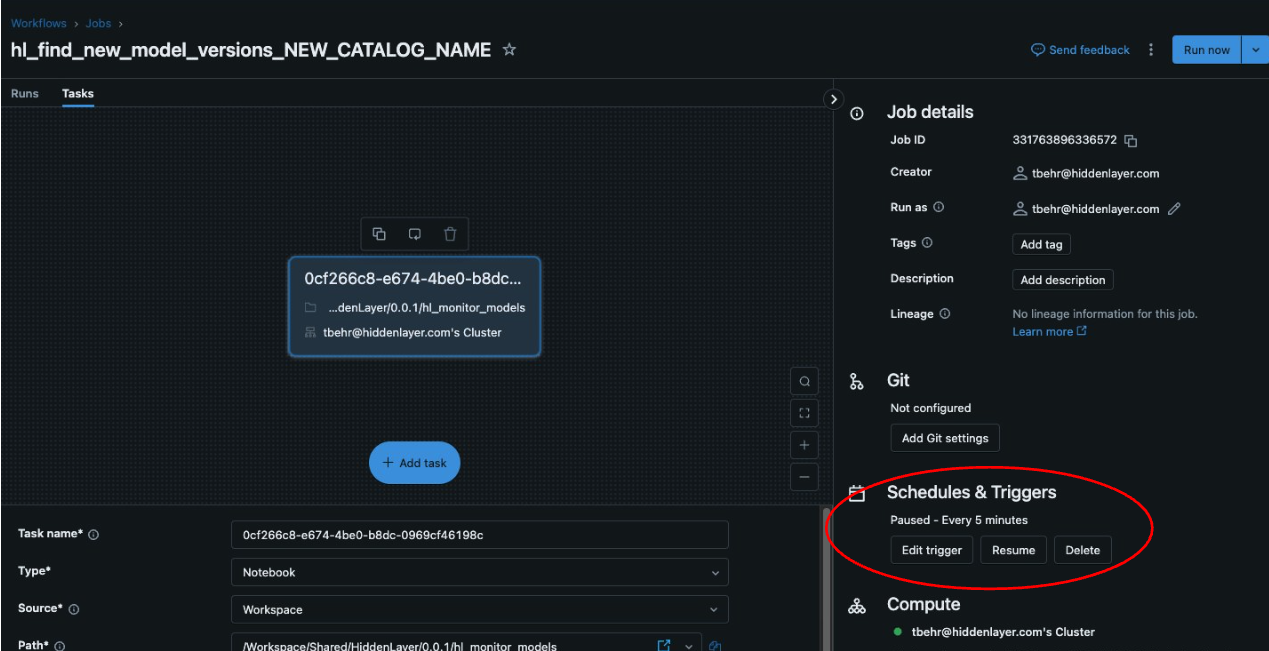
Use the dropdown to edit the schedule to your desired interval.
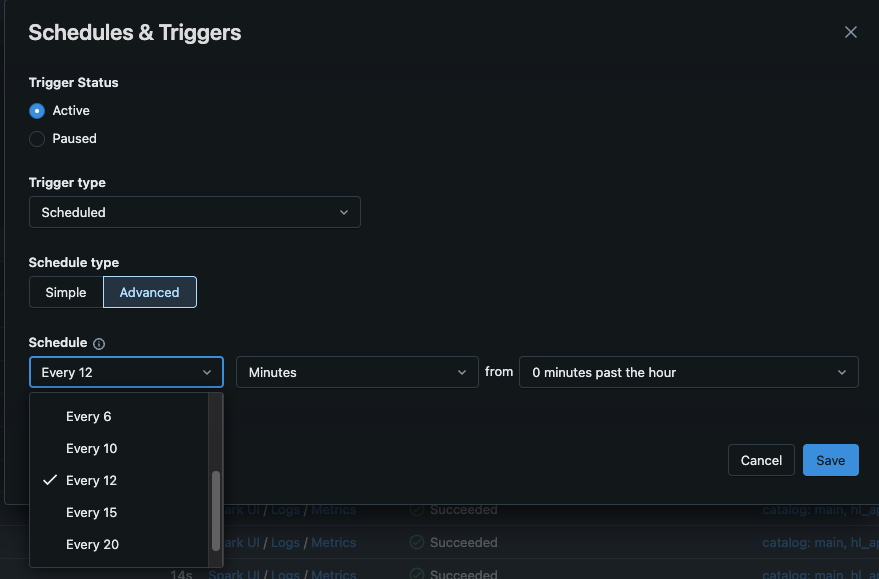
Click Save.
The HiddenLayer orchestrator integration allows you to scan multiple models simultaneously. By default, the "MAX_ACTIVE_SCAN_JOBS" field is set to 10, which controls the number of concurrent jobs that can be processed at once. If you need to adjust this number, follow these steps:
- Navigate to the workspace and locate the shared repository.
- Inside the repository, find the hiddenlayer folder, then open the hl_monitor_models folder.
- Scroll down to the "MAX_ACTIVE_SCAN_JOBS" field and modify the value to the desired number of concurrent jobs.
Keep in mind that while the HL modscan system has a queueing mechanism to handle large numbers of jobs, increasing the number of active jobs can put additional strain on your disk space and network bandwidth. Adjust the value carefully based on your system’s capacity to avoid potential performance issues.
This script is designed to interact with MLflow to remove the "unscanned" tag from model versions within a specific catalog and schema. This script automates the process of scanning models and ensures that any model marked as "unscanned" is automatically processed for rescan.
- Fetch Registered Models: The script retrieves all registered models from MLflow.
- Filter by Schema: It checks if the models belong to a specific schema within a catalog.
- Check Model Versions: For each model, it fetches all versions and checks for the presence of the "hl_scan_status" tag with the value "unscanned".
- Delete the Tag: If the tag is found, it deletes it, triggering a rescan for the model version.
- Rescan Triggered: Removing the
"unscanned"tag effectively triggers a rescan of the model by the HiddenLayer Model Scanner job.
import mlflow
from mlflow.tracking import MlflowClient
HL_SCAN_STATUS = "hl_scan_status"
UNSCANNED = "unscanned"
CATALOG_NAME = "ADD_CATALOG_NAME_HERE"
SCHEMA_NAME = "ADD_SCHEMA_NAME_HERE"
client = MlflowClient()
def delete_unsanned_tag_from_all_models_in_default_schema():
print("Fetching all registered models...")
registered_models = client.search_registered_models()
if not registered_models:
print("No registered models found.")
return
for model in registered_models:
model_name = model.name
print(f"Found model: {model_name}")
if model_name.startswith(f"{CATALOG_NAME}.{SCHEMA_NAME}."):
print(f"Model {model_name} is in the '{SCHEMA_NAME}' schema of the '{CATALOG_NAME}' catalog.")
print(f"Fetching all versions for model {model_name}...")
model_versions = client.search_model_versions(f"name='{model_name}'")
if not model_versions:
print(f"No versions found for model {model_name}. Skipping.")
continue
for model_version in model_versions:
print(f"Checking version {model_version.version} for model {model_name}...")
model_version_details = client.get_model_version(model_name, model_version.version)
tags = model_version_details.tags
if not tags:
print(f"No tags found for model {model_name} version {model_version.version}.")
else:
print(f"Found tags for model {model_name} version {model_version.version}: {tags}")
for tag_key, tag_value in tags.items():
print(f"Checking tag: {tag_key} = {tag_value}")
if tag_key == HL_SCAN_STATUS and tag_value == UNSCANNED:
print(f"Tag '{HL_SCAN_STATUS}={UNSCANNED}' found on model {model_name} version {model_version.version}. Deleting...")
client.delete_model_version_tag(model_name, model_version.version, HL_SCAN_STATUS)
print(f"Tag '{HL_SCAN_STATUS}={UNSCANNED}' deleted from model {model_name} version {model_version.version}")
else:
print(f"Tag '{HL_SCAN_STATUS}={UNSCANNED}' not found on model {model_name} version {model_version.version}.")
def scan_and_delete_tags():
delete_unsanned_tag_from_all_models_in_default_schema()
scan_and_delete_tags()Navigate to the Workspace:
- Log in to your Databricks workspace.
- In the left-hand sidebar, click on Workspace to open the workspace view.
Go to the HiddenLayer Folder:
- In the Workspace, navigate to the Shared folder.
- Inside the Shared folder, find and open the HiddenLayer folder.
- Inside the HiddenLayer folder, locate the folder for the specific version number you are working with and open it.
Open the hl_scan_model File:
- Find and select the file named hl_scan_model within the version folder.
Add the Code Block:
- Scroll to the very end of the hl_scan_model file and add the following block of code.
catalog = full_model_name.split(".")[0] modelName = full_model_name.split(".")[2] if scan_results.severity != "safe": new_schema = "quarantine_danger" new_model_name = f"{catalog}.{new_schema}.{modelName}" mlflow.register_model( f"models:/{full_model_name}/{model_version_num}", new_model_name ) print(f"Model moved to: {new_model_name}") mv = get_model_version(new_model_name, 1) tag_model_version_with_scan_results(mv, scan_results) mlflow.MlflowClient().delete_registered_model(full_model_name) print("Model deleted from initial schema") raise Warning("High threat level detected -- model moved to quarantine. Please review the scan results.") else: new_schema = "safe" new_model_name = f"{catalog}.{new_schema}.{modelName}" mlflow.register_model( f"models:/{full_model_name}/{model_version_num}", new_model_name ) print("No detections by model scanner") mv = get_model_version(new_model_name, 1) tag_model_version_with_scan_results(mv, scan_results) print(f"Model moved to: {new_model_name}") mlflow.MlflowClient().delete_registered_model(full_model_name) print("Model deleted from initial schema")Update the Schema Locations (Optional):
- On line 5, update the new_schema variable to specify the location of the quarantine_danger schema where unsafe models should be moved.
- On line 20, update the new_schema variable to specify the location of the safe schema where models with no detections should be moved.
Save the file.
- After adding the code, click Save to save the updated hl_scan_model file.
- The script checks the results of each scanned model.
- If the model's scan results show any severity other than "safe," it moves the model to the quarantine_danger schema and deletes it from the original location.
- If the model is safe, it moves the model to the safe schema.
- The model is then re-registered in the appropriate schema, and its scan results are tagged.
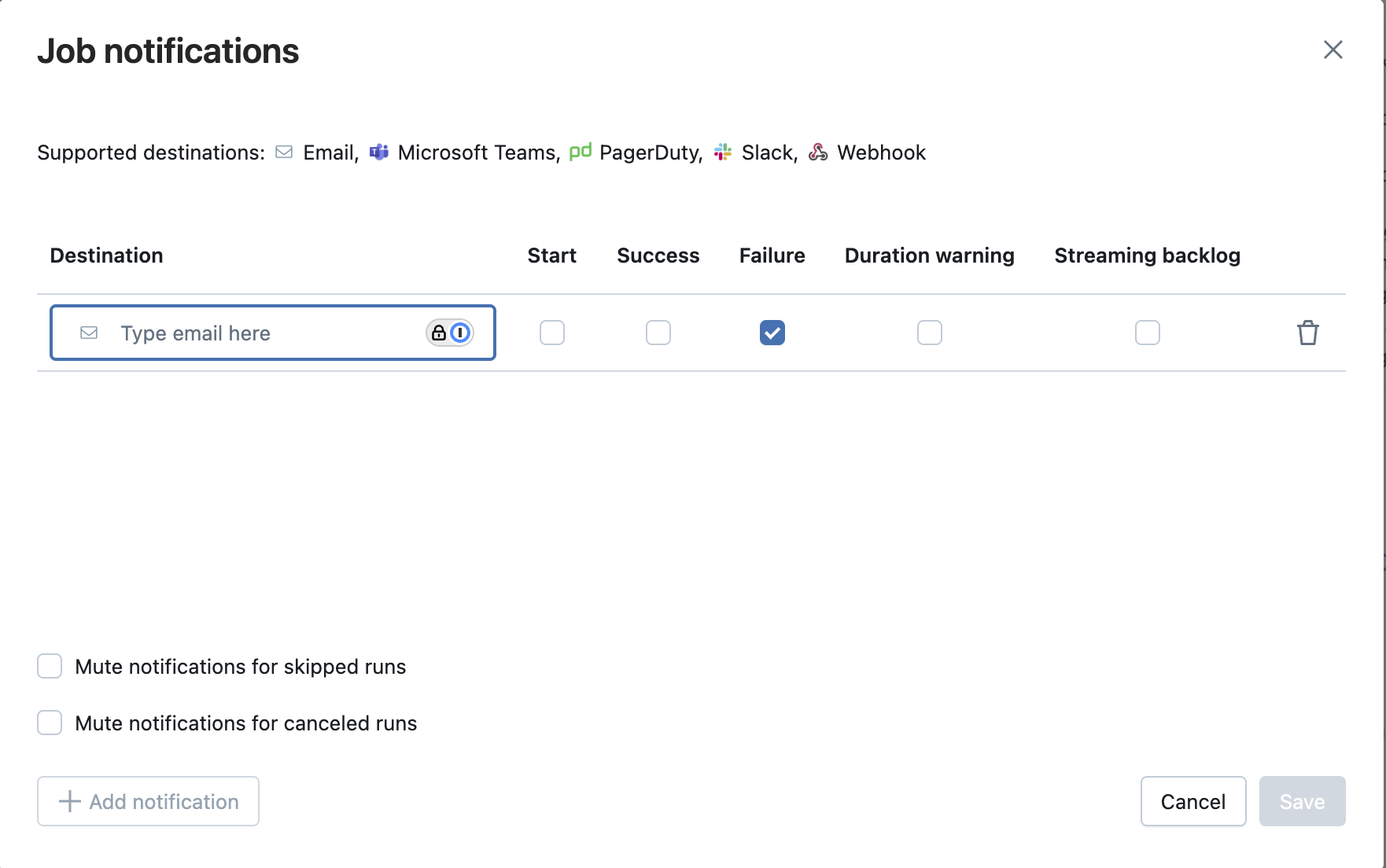
Enable job failure alerts in Databricks by adding a notification in the job settings that triggers an email or webhook whenever the job fails.
Go to your job in Databricks.
Scroll to the Job Notifications section.
Click Edit notifications.
Select your options:
- On failure (or success, skipped, etc.)
- Enter recipients (email, webhook, Slack, etc.)
Click Save.
Scan jobs are failing with authentication errors.
Your HiddenLayer API client ID and client secret have an expiry. When these expire, scan jobs will start failing with authentication errors. To resolve this, generate a new HiddenLayer API client ID and client secret, then update the Databricks secret store. Do not change the secret name because this is part of the Databricks job configuration.